News
2020-08-18: PyGPlates beta revision 28 released
This pyGPlates beta release adds support for Python 3 (in addition to Python 2.7).
What's new in pyGPlates revision 28:-
- Pre-built pyGPlates libraries for Windows and macOS supporting:
- Python 2.7
- Python 3.5
- Python 3.6
- Python 3.7
- Python 3.8
- macOS libraries signed and notarized by Apple:
- Should no longer get security prompts (including macOS Catalina).
- Ubuntu packages for 16.04 LTS (Xenial), 18.04 LTS (Bionic), 19.10 (Eoan) and 20.04 LTS (Focal).
- Python 2 and 3 (32-bit and 64-bit), except Focal (Python 3 64-bit only).
- Create topological features (dynamic lines, polygons and deforming networks):
- Usually they are built in GPlates, but this can now be done in pyGPlates.
- See the sample code.
- Supports deforming trenches when used with subduction convergence script.
- Much faster querying of reconstructions.
- Bug fixes.
Download this release from the Download page.
The pyGPlates documentation and tutorials are available on the User Documentation page and includes:
- an introduction to pyGPlates,
- an installation guide,
- a 'Getting Started' tutorial,
- documented sample code,
- foundations of pyGPlates, and
- a detailed reference of pyGPlates functions and classes.
The pyGPlates tutorials are Jupyter Notebooks that analyse and visualise real-world data using pyGPlates. These tutorials complement the sample code in the pyGPlates documentation by providing a more research-oriented focus.
PyGPlates enables access to GPlates functionality via the Python programming language. This may be of particular use to researchers requiring more flexibility than is provided by the GPlates user interface.
PyGPlates compiles and runs on Windows 10, macOS 10.13+ and Linux.
2019-08-30: GPlates 2.2 released
A few points to note regarding this release:-
- The Sample Data includes the Matthews et al. (2016) model, which has been updated to include the corrections to the Pacific rotations prior to 83 Ma according to Torsvik et al. (2019). Please update your local datasets.
- Matthews, K. J., Maloney, K. T., Zahirovic, S., Williams, S. E., Seton, M., and Müller, R. D., 2016, Global plate boundary evolution and kinematics since the late Paleozoic: Global and Planetary Change, DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.10.002
- Torsvik, T.H., Steinberger, B., Shephard, G.E., Doubrovine, P.V., Gaina, C., Domeier, M., Conrad, C.P. and Sager, W.W., 2019. Pacific-Panthalassic reconstructions: Overview, errata and the way forward. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, DOI:10.1029/2019GC008402
- There is now a 64-bit version of GPlates for Windows:
- The 64-bit Windows installer works on 64-bit versions of Windows 7/8/8.1/10.
- The 32-bit Windows installer works on 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows 7/8/8.1/10.
- Currently there are some issues with 3D scalar fields on macOS Mojave (10.14) and above:
- This happens on some Macs with AMD graphics (specifically we've noticed AMD Radeon Pro 460).
- 3D scalar fields render incorrectly and then crash in the graphics driver.
- Note that disabling automatic GPU switching does not help, since this always uses the discrete graphics (eg, AMD) and not the integrated graphics (eg, Intel HD).
- Also, the first time you open GPlates on macOS 10.12 Sierra (and above) you will need to Control-click (or right click) and select Open.
What's new in GPlates 2.2:-
- Deformation:
- Option to generate 'exponential' stretching profiles across rifts (instead of default constant stretching).
- Activated by adding 'rift' left/right plate IDs to any deforming network.
- Optionally specify three control parameters:
- One parameter controls the exponential constant.
- The other two parameters control how closely to approximate exponential curve (with better approximations running slower).
- Calculate, visualize and export strain rate "style":
- A unit-less quantity defined in Kreemer et al. 2014, categorizing extension, contraction and strike-slip.
- Support deforming networks in Net Rotation export (in addition to rigid plates).
- Option to generate deforming mesh points inside interior rigid blocks in deforming networks.
- Option to generate 'exponential' stretching profiles across rifts (instead of default constant stretching).
- Topologies:
- Updated CitcomS topology export:
- Option to export all (plate/network/slab) polygons and all (plate/network/slab) boundary segments.
- Fixed missing plates (that were not of type TopologicalClosedPlateBoundary; eg, OceanicCrust).
- Updated General topology export:
- Option to export boundary segments.
- Including separate subduction, subduction left/right, ridge/transform files (similar to CitcomS topology export).
- Boundary segments are not duplicated.
- Option to export boundary segments.
- Robust determination of velocities along topological boundaries (of rigid plates and deforming networks):
- Notably in the presence of deforming *lines* (eg, topological lines made from independently moving points).
- Results in robust strain rates in topological networks (especially at intersecting boundary corners).
- Updated CitcomS topology export:
- Projects and recent sessions:
- Save time slider range to project/session.
- Also extend default time range to 410Ma (from 200Ma) for rotation model in sample data.
- Save time slider range to project/session.
- File formats:
- Can load/save GeoPackage geometry files.
- All non-GPML geometry formats (Shapefile, etc) no longer force a feature to have all mapped properties:
- Avoids adding a property to a feature that it didn't have (eg, conjugate plate ID).
- Support UTF8 when loading (and saving) PLATES4 line and rotation formats.
- Useful when rotation comments contain non-ASCII characters.
- Rendering:
- Can show/hide rasters, 3D scalar fields and scalar coverages.
- In "View > Geometry Visibility" menu.
- Can show/hide topological lines, polygons and networks (in same menu).
- Can also show/hide topological 'sections' (those geometries contributing to topological boundaries/interiors).
- So only see final continuously-closed topological boundaries.
- GPlates now hides these dangling pieces by default (advanced users can change the default though).
- Can also show/hide topological 'sections' (those geometries contributing to topological boundaries/interiors).
- Velocity layers can calculate/visualize velocities on *domains* that are topology layers (as opposed to *surfaces*).
- At the *vertices* of topological lines, polygons and networks.
- Render clicked (white) geometries on top of non-clicked (grey) geometries (belonging to the same feature).
- Useful when the feature's geometries overlap.
- Can show/hide rasters, 3D scalar fields and scalar coverages.
- GPlates Geological Information Model (GPGIM):
- Added new GPGIM feature type 'DeformingRegionEdge' that is edge of a deforming region but not also a plate boundary.
- Allow MeshNode feature to contain a point geometry (previously only allowed a multi-point).
- Enables single point to automatically create a velocity layer (because only MeshNode features do this).
- Added properties for rift exponential stretching:
- 'riftLeftPlate' and 'riftRightPlate' - conjugate rigid plates bounding a rift topological network.
- 'riftExponentialStretchingConstant' - controls exponential variation across rift stretching profile.
- 'riftEdgeLengthThresholdDegrees' and 'riftStrainRateResolutionLog10' - control approximation to true exponential curve.
- Removed topological network properties 'networkMaxEdge' and 'networkShapeFactor' (no longer used).
- Geometry tests:
- Assigning plate IDs is much faster (especially dense geometries like coastlines).
- Robust polyline intersection testing, and significantly faster.
- Distances to polygons (from another geometry) now take into account any interior rings of the polygon.
- Bug fixes:
- Fixed hang on start up on some Mac systems (where network interface appears active but network is unavailable).
- Fixed time-dependent raster import (and 3D scalar field import) not accepting filenames with uppercase extensions.
- Fixed crash triggered when exporting total strains.
- Fixed crash when exiting GPlates on some Ubuntu versions (due to freeing same memory twice).
- Fixed crash when saving a rotation feature with a 'gml:name' or 'gml:description' property to a PLATES4 rotation file.
- Fix crash loading a GPML file containing a feature property that cannot be interpreted using any property defined in the GPGIM.
- Build:
- Support Visual Studio 2015/2017 (GDAL 2.3 uses C++11 which requires VS2015), and update Windows build docs accordingly.
- Fixed incorrect 90 degree rotation of rasters with inbuilt projections (eg, Lambert Conformal Conic) when GPlates compiled with GDAL 3.0.
- Upgraded support to new Proj6 API (also support deprecated Proj4 API).
- Added SQLite3 dependency library (due to adding support for GeoPackage vector format).
- Support Boost 1.66 (added x32/x64 architecture tags) and Boost 1.67 (added Python version suffix 'python27').
- Fixed CMake error finding GMP library on Windows (recent CGAL versions already link to GMP, so GPlates doesn't need to).
- Work around internal compiler error (gcc 5.4) on Ubuntu Xenial (16.04).
- No longer combine '-ansi' (equivalent to '-std=c++98') and '-std=c++11' flags (first noticed on gcc 9.1).
- No longer turn warnings into errors:
- There are lots of warnings generated by dependency libraries (that we can't easily fix), and by new compilers.
...and other changes listed in the CHANGELOG file in the GPlates source-code releases.
GPlates 2.2 compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1/10, Linux and MacOS X.
Download GPlates 2.2 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available, and has been updated for the GPlates 2.2 release. For more information, see the Download page.
2018-08-08: GPlates 2.1 and pyGPlates beta revision 18 released
This release contains both GPlates 2.1 and pyGPlates beta revision 18.
- Please use this pyGPlates release when working with any data saved by GPlates 2.0 or GPlates 2.1 (especially topologies).
- This will avoid incorrect reconstruction of half-stage rotation features (such as mid-ocean ridges) created by GPlates 2.0 (or above).
- There are no major new features in this pyGPlates release, it is mostly for compatibility with GPlates 2.0 (and above).
What's new in GPlates 2.1:-
- Velocity legend:
- Visual indicator of velocity arrow lengths in a target velocity layer.
- Displays a single arrow and its velocity (in cm/yr).
- Legend velocity can be constant (eg, 2 cm/yr), or variable (to keep arrow length within reasonable limits).
- Legend arrow length changes in response to velocity scaling in the target layer.
- Projects and recent sessions:
- Fixed problems loading projects saved on computers with different locales:
- The following backward/forward compatibility rules now apply:
- Can load the following on 2.1:
- Projects saved with 2.1 on any locale:
- For example, (English or Chinese)->(English or Chinese).
- Only projects saved with 2.0 on English locale or same locale (if not English):
- For example, English->(English or Chinese), or Chinese->Chinese.
- Projects saved with 2.1 on any locale:
- Can load the following on 2.0:
- Projects saved with 2.1 on any locale, but must be loaded on English locale.
- For example, (English or Chinese)->English.
- Only projects saved with 2.0 on matching locale.
- For example, English->English or Chinese->Chinese.
- Projects saved with 2.1 on any locale, but must be loaded on English locale.
- Can load the following on 2.1:
- The following backward/forward compatibility rules now apply:
- Save anchored plate ID, background colour and graticule settings to project/session.
- When asked to locate a missing data file, show directory where missing file should have been.
- Fixed problems loading projects saved on computers with different locales:
- Deformation:
- Topological networks:
- Can now use mid-ocean ridges as boundary/interior sections.
- Added triangulation *draw* mode in topology network (brown) layers.
- Can draw boundary, mesh or fill (independently of colour mode).
- Display mesh by default (instead of boundaries).
- Better visual indicator of deforming regions.
- Can draw boundary, mesh or fill (independently of colour mode).
- Deforming meshes now appear in 2D map views when strain rate smoothing enabled.
- Strain rate and accumulated strain:
- Added total strain rate.
- Visualize and export.
- Uses geodesy definition of second invariant in Kreemer et al. 2014.
- Added exports for the following accumulated strain quantities:
- Strain dilatation.
- Principal strain and stretch.
- Exports triplet (angle/azimuth, major axis and minor axis).
- Major/minor axes are strain (extension positive; compression negative) or stretch (1.0 + strain; always positive).
- Plot stretch ellipses in GMT (with psxy).
- Added optional strain rate clamping:
- Useful for excessively high strain rates in some triangles of deforming mesh.
- Clamps *total* strain rate, since includes both normal and shear components.
- All strain rate and accumulated strain quantities now calculated in spherical coordinates (instead of 2D cartesian).
- Finite strain is now correctly accumulated.
- By integrating deformation gradient tensor over time, using spatial gradients of velocity.
- Added total strain rate.
- Crustal thinning:
- Fixed crustal thinning (gamma) factor.
- Should be '1 - T/T_initial' instead of 'T/T_initial'.
- Automatically convert crustal thinning factors created by GPlates 2.0 (when loading GPML file).
- Added crustal stretching (beta) factor 'T_initial/T'.
- All three crustal thickness types now created when generating crustal thickness points.
- Thickness (kms), stretching (beta) factor and thinning (gamma) factor.
- Independently visualize and export.
- Can optionally generate points within a lat-lon box.
- Calculate statistics using entire history of crustal thicknesses/factors (instead of just at initial time).
- Provides a better mapping of palette colours.
- Fixed missing IMPORT_AGE attribute in OGR vector formats (eg, Shapefile).
- Required for crustal thickness points to work propertly (and half-stage rotations).
- Fixed crustal thinning (gamma) factor.
- Added option to remove points from within a deforming network as soon as they fall outside.
- Fixed symbols not working for points when they are reconstructed using topologies.
- Topological networks:
- Rasters:
- Enable import and export of NetCDF version 4 rasters (via GDAL library version 2).
- Interoperable with GMT version 5.
- Optionally compress exported NetCDF.
- Support export of *gridline* registered rasters.
- Eg, global raster where left and right pixel columns overlap on dateline.
- Support greater than 8-bit per channel RGBA rasters (including floating-point).
- Import generates transparency for RGBA rasters supporting no-data values (in each R,G,B,A band).
- Time-dependent raster (and 3D scalar field) import now supports times (depths) anywhere in filenames.
- For ambiguous cases (eg, multiple decimal points) place times (depths) at end of filename (after '_' or '-').
- Fixed incorrect half-pixel shift downwards (North to South) for *gridline* registered global GMT grids.
- Has been incorrectly shifting since GPlates 1.4.
- Fixed semi-transparent vertical seam near North and South poles at longitude 0 or -180.
- Happened in 2D map views (and in 3D globe view when reconstructing raster).
- Fixed slow rendering of very coarse rasters in 2D map views.
- Enable import and export of NetCDF version 4 rasters (via GDAL library version 2).
- Velocities:
- Make GMT velocity export compatible with GMT psxy "-Sv" and "-SV" command-line options.
- Angle/azimuth now in column 3 and magnitude in column 4.
- Optional plate ID now in column 5.
- Make GMT velocity export compatible with GMT psxy "-Sv" and "-SV" command-line options.
- Colouring:
- CPT files:
- Support GMT5 "C/M/Y/K" colours and CMYK "COLOR_MODEL".
- Support different colour types on a single line (eg, "R/G/B" and "gray80").
- Added button to reload CPT file in colouring/draw styles.
- Assign *all* known feature types a random colour in Feature Type draw style.
- From GPlates 1.3 to 2.0 inclusive, all but 11 feature types were incorrectly assigned the default navy colour.
- CPT files:
- Digitization:
- Fixed vertex edits not modifying topologies.
- Eg, moving vertices of a feature used as a topological section in a topological network.
- Digitize New Geometries:
- No longer offer Reconstruction/Conjugate Plate IDs for topological networks and topological lines.
- Only meaningful for topological polygons (eg, to calculate non-deforming plate velocities).
- No longer offer Reconstruction/Conjugate Plate IDs for topological networks and topological lines.
- Fixed vertex edits not modifying topologies.
- Geometry tests:
- Point-in-polygon test now considers points *on* a polygon edge (within extremely small tolerance) to be inside polygon.
- Helps ensure points lying exactly on dateline are inside a polygon that has an edge exactly aligned with dateline.
- Fixed Assign Plate IDs retaining only first geometry in each feature when using 'copy by overlap'.
- Fixed point proximity to a polyline/polygon in rare situations.
- Resulted in incorrect selection with Choose Feature tool.
- Point-in-polygon test now considers points *on* a polygon edge (within extremely small tolerance) to be inside polygon.
- Topology tools:
- Build topology tools are now always enabled (makes it easier to build topologies at any time).
- GPlates Geological Information Model (GPGIM):
- Loosen constraints on properties that can be loaded from a GPML file.
- Any feature type can now contain any property defined in the GPGIM.
- Can have feature types not defined in GPGIM.
- More aligned with current ability to add any property to any feature type (albeit with a warning message).
- Also more aligned with Shapefiles (which can load any property, in Shapefile mapping, into any feature type).
- Allow multiple 'gpml:boundary' polygons per feature.
- Loosen constraints on properties that can be loaded from a GPML file.
- Graphics (OpenGL):
- Only disable surface mask functionality in 3D scalar fields for problematic graphics driver/hardware.
- Only affects surface masking of scalar fields (not all scalar field functionality).
- Only disable surface mask functionality in 3D scalar fields for problematic graphics driver/hardware.
- Support up to 10-digit plate IDs (essentially 32-bit signed integers) in all Plate ID spin boxes.
- Fixed inability to save PLATES rotation files using non-ASCII (unicode) filenames (in some cases).
- Fixed inability to save/load OGR formats (eg, Shapefile) to/from non-ASCII (unicode) filenames.
...and other changes listed in the CHANGELOG file in the GPlates source-code releases.
GPlates 2.1 compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1/10, Linux and MacOS X.
Download GPlates 2.1 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available, and has been updated and extended in many ways for the GPlates 2.1 release. For more information, see the Download page.
PyGPlates enables access to GPlates functionality via the Python programming language. This may be of particular use to researchers requiring more flexibility than is provided by the GPlates user interface.
The pyGPlates binaries currently require Python 2.7, however the pyGPlates source code now works with Python 3. PyGPlates compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1, Linux and MacOS X.
Download pyGPlates beta revision 18 from the Download page.
The pyGPlates documentation and tutorials are available on the User Documentation page and includes:
- an introduction to pyGPlates,
- an installation guide,
- a 'Getting Started' tutorial,
- documented sample code,
- foundations of pyGPlates, and
- a detailed reference of pyGPlates functions and classes.
The pyGPlates tutorials are Jupyter Notebooks that analyse and visualise real-world data using pyGPlates. These tutorials complement the sample code in the pyGPlates documentation by providing a more research-oriented focus.
2016-11-18: GPlates 2.0 released
What's new in version 2.0:-
- Projects and recent sessions:
- Now saves and restores all layer information:
- Including layer order, visibility and all settings within each layer (such as colour styles and colour palette filenames).
- Open projects using File menu, drag'n'drop, double-clicking or command-line.
- Project name displayed in window title.
- Copy a project to another computer. For example:
- Zip up a folder containing project file and associated data files (including colour palette files).
- Unzip to another computer and open project file.
- Option to locate missing data files (when loading project or recent session):
- Useful when data files moved since project or session was saved.
- Option to resolve ambiguous data filenames (when loading relocated project):
- Useful when data files exist in both original and relocated locations.
- GPlates 2.0 can open projects and recent sessions saved by all prior versions of GPlates:
- However information saved by earlier versions is limited.
- GPlates 1.5 can open projects and recent sessions saved by GPlates 2.0:
- However restored information is limited (to what GPlates 1.5 can understand).
- Now saves and restores all layer information:
- Deformation:
- Topological networks:
- Boundary is similar to a topological closed plate boundary, but also has:
- A deforming interior region (due to individual deforming points).
- Optional interior rigid blocks.
- Build New Network Topology tool now publicly available (without requiring command-line switch to enable).
- Export topological network boundaries in general Resolved Topologies export.
- Query and visualise velocities and strain rates at arbitrary points in networks.
- Optionally display total (accumulated) strain at arbitrary points:
- Displays principal components and orientation.
- Outward-facing red arrows for extension.
- Inward-facing blue arrows for compression.
- Boundary is similar to a topological closed plate boundary, but also has:
- Reconstructing regular features using topologies:
- Use both topological rigid plates and deforming networks to reconstruct regular features.
- Incrementally reconstructs by plate ID in topological rigid plates.
- Incrementally deforms in topological deforming networks.
- Begin incremental reconstruction at a feature's time of appearance, digitisation time or present day.
- Use specific topological layers or default to all loaded topologies.
- Option to detect lifetime of each point in a geometry:
- Oceanic points appear (mid-ocean ridges) and disappear (subduct).
- Based on convergence velocity and distance to plate boundary during a plate/network transition.
- Scalar coverages:
- A new geometry type in a new layer type.
- Each point in a multipoint/polyline/polygon has a scalar value associated with it.
- For example, visualise mid-ocean ridge spreading rates and asymmetry calculated externally using pyGPlates.
- Crustal thinning:
- A specific type of scalar coverage containing crustal thickness values.
- GPlates recognises this coverage type internally:
- Uses deformation strain rates to evolve crustal thickness over time.
- An input dialog generates initial crustal thickness points:
- Uniform distribution of points within a topological rigid plate or deforming network boundary (with optional random offset).
- Specify initial constant/flat crustal thickness at a past geological time.
- Choose from a selection of built-in colour palettes to visualise crustal thickness variations over time.
- Export crustal thickness values to GMT(xy) or GPML format.
- Also added a separate export for deformation (strain rates).
- Topological networks:
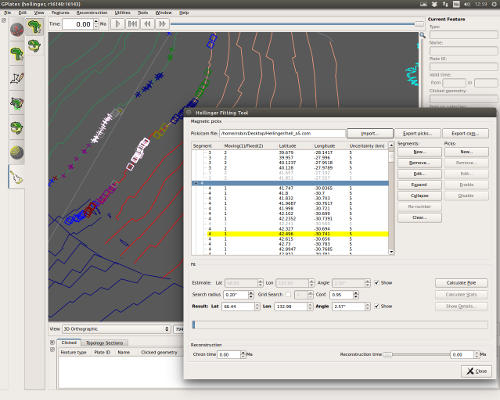
- New Hellinger tool:
- GPlates has a new workflow to determine best-fitting poles by the method of Hellinger:
- Import and export data files compatible with the FORTRAN programs of Chang and co-workers.
- Edit and create magnetic pick data points, via the canvas or tabularly via the Hellinger dialog.
- Adjust segmentation of magnetic picks.
- Enable/disable magnetic picks from inclusion in the fitting algorithms.
- Specify pole and angle estimates via the canvas or via the Hellinger dialog.
- Perform fitting using a python implementation the FORTRAN programs.
- Visualise resulting fit and uncertainty on the canvas.
- Export fit and uncertainty data to text file.
- GPlates has a new workflow to determine best-fitting poles by the method of Hellinger:
- GPlates now calculates and exports net rotation of the lithosphere (based on the method of Torsvik et al., 2010) using global coverages of dynamic plate polygons.
- Net rotations are exported via the standard "Export…" tool, and by selecting the "Net rotation" export type.
- Any dynamic plate-polygon data sets currently active in GPlates will be used as the basis for net rotation calculations.
- No longer require command-line switch to enable importing of 3D scalar fields.
- Latest improvements:
- Reads georeferencing and spatial reference system (SRS) from first depth layer during import.
- Frees disk space after import (removes cached depth layer rasters).
- Fixed flickering cross-sections.
- Fixed SVG export of isosurfaces (on Mac OS X).
- GPlates now has more complete support for OGR-supported files (e.g. ESRI shape file, OGR-GMT and others) which provide spatial reference system / projection information.
- Any SRSs supported by the PROJ4 library should now be accepted by GPlates.
- When saving to a file which had a non-WGS84 SRS associated with it, GPlates will prompt the user to export in either the original SRS, or in WGS84.
- All other forms of file export in GPlates continue to use WGS84.
- Contain interior holes.
- Supported in file input/output, raster reconstruction, filled polygons, 3D scalar fields, etc.
- Available in raster, 3D scalar field and scalar coverage layers.
- Remap the range using mean and standard deviation of the layer data (raster, 3D scalar field or scalar coverage).
- Added a variety of built-in colour palettes based on ColorBrewer sequential and diverging colour scales.
- Improved stability and speed when connecting raster layer to polygons layer.
- Removed raster seams/cracks between adjacent polygons.
- Using the new visibility icons in the Layers dialog.
- Changes to spreading asymmetry, after digitisation, no longer incorrectly reposition ridge.
- GPlates now stores the last used directory for Project files.
- In addition, there is more fine-grained support for both Feature Collection and Project folder preferences.
- These can be adjust through the Preferences (Ctrl+,) dialog.
- Supported for various feature types in GPlates Geological Information Model (GPGIM).
- Find-as-you-type named ages with timescale colouring.
...and other changes listed in the CHANGELOG file in the GPlates source-code releases.
GPlates 2.0 compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1/10, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 2.0 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2016-02-04: PyGPlates beta revision 12 released
Welcome to the first beta release of the GPlates Python library known as pyGPlates.
PyGPlates enables access to GPlates functionality via the Python programming language. This may be of particular use to researchers requiring more flexibility than is provided by the GPlates user interface.
The following pyGPlates functionality is available:-
- Load and save feature data (GPML, Shapefile, etc).
- Create/modify/query feature data.
- Traverse/modify/query plate rotation hierarchy.
- Partition into plates and assign plate properties.
- Reconstruct geometries, flowlines, motion paths.
- Resolve topological plates and query their boundary sections (ridges/subductions).
- Calculate velocities.
- Distance between geometries (region-of-interest queries).
- Geometry queries (length, point-in-polygon, area, centroid, tessellate, interpolate, join, partition).
Download this release from the Download page. It supports Python 2.7. And compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1, Linux and MacOS X.
The pyGPlates documentation and tutorials are available on the User Documentation page.
The pyGPlates documentation includes:
- an introduction to pyGPlates,
- an installation guide,
- a 'Getting Started' tutorial,
- documented sample code,
- foundations of pyGPlates, and
- a detailed reference of pyGPlates functions and classes.
The pyGPlates tutorials are Jupyter Notebooks that analyse and visualise real-world data using pyGPlates. These tutorials complement the sample code in the pyGPlates documentation by providing a more research-oriented focus.
2015-03-11: GPlates 1.5 + hellinger-testing released
What's new in version 1.5 + hellinger-testing:-
- New Hellinger tool:
- Added new workflow to determine best-fitting poles by the method of Hellinger:
- Import and export data files compatible with the FORTRAN programs of Chang and co-workers.
- Edit and create magnetic pick data points, via the canvas or tabularly via the Hellinger dialog.
- Adjust segmentation of magnetic picks.
- Enable/disable magnetic picks from inclusion in the fitting algorithms.
- Specify pole and angle estimates via the canvas or via the Hellinger dialog.
- Perform fitting using a Python implementation the FORTRAN programs.
- Visualise resulting fit and uncertainty on the canvas.
- Export fit and uncertainty data to text file.
This experimental release of GPlates contains a new Hellinger tool in addition to all functionality available in the recent GPlates 1.5 official release.
This release compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1, Linux and MacOS X. Download this release from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2015-02-14: GPlates 1.5 released
What's new in version 1.5:-
- Projects:
- Save and restore your sessions with project files.
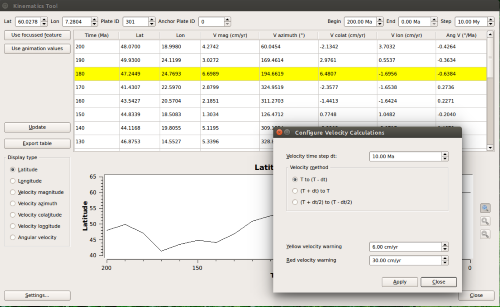
- New kinematics tool:
- Displays table of latitude, longitude, velocity, and velocity-related quantities for a given lat-lon point, plate ID, and range of times.
- Displays graph of above quantities against time.
- Exports table to text file.
- Kinematic tool settings dialog to change details of the velocity calcliations.
- Kinematic tool settings are saved in user preferences.
- Auto-fills point data from focussed feature.
- Auto-fills time ranges from animation settings.
- Import and export GeoJSON format feature collections.
...and other changes listed in the CHANGELOG file in the GPlates source-code releases.
GPlates 1.5 compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.5 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2014-04-18: GPlates 1.4 released
What's new in version 1.4:-
- Export numerical and colour reconstructed rasters:
- Exports each visible raster layer to a separate raster file.
- User specified latitude/longitude export region and pixel resolution.
- Numerical export writes floating-point data:
- Supported raster formats: NetCDF, GMT NetCDF, GeoTIFF and Erdas Imagine.
- Standard use of not-a-number (NaN) for pixels not covered by reconstructed raster.
- Colour export:
- New supported colour raster formats: GeoTIFF and Erdas Imagine.
- Uses per-layer colour palette as needed.
- Includes surface relief lighting.
- Exports each visible raster layer to a separate raster file.
- Import raster improvements:
- New import raster formats: ERMapper, Erdas Imagine and GeoTIFF.
- Imports georeferencing from source raster file.
- Supports inbuilt raster spatial reference system:
- Includes projections (for example, Lambert Conformal Conic).
- Improved performance when importing very large rasters and displaying in 2D map views.
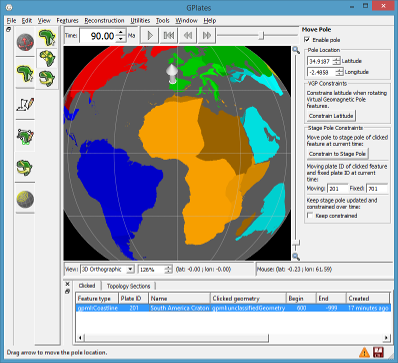
- New Move Pole canvas tool:
- Supports Modify Reconstruction Pole canvas tool:
- by allowing user to specify location of pole used for rotation adjustments.
- Drag pole location with mouse or enter text coordinates.
- Optionally constrain pole location to moving/fixed stage pole of clicked feature.
- Includes tracking stage pole over time.
- Supports Modify Reconstruction Pole canvas tool:
- Velocity smoothing near plate boundaries.
- Mid-ocean ridges:
- Supports spreading asymmetry.
- More accurate half-stage rotation.
- Needed in some rare cases.
- Volume visualisation of 3D scalar fields (continued early preview functionality):
- To be officially released in GPlates 1.5.
- This release (1.4) adds preview functionality (since 1.3) available to advanced users:
- Requires the "--enable-scalar-field-import" command-line switch to enable scalar field import.
- For example, "cd C:\Program Files (x86)\GPlates\GPlates 1.4.0" and "gplates-1.4.0.exe --enable-scalar-field-import".
- Enables menu item 'File -> Import -> Import 3D Scalar Field...'
- Preliminary support for 'regional' (non-global) scalar fields.
- Colour palette improvements:
- Optionally remap scalar/gradient palette range.
- Adjust range using mean and standard deviation of scalar field.
- Supports transparent colours for isosurface and cross sections.
...and other changes listed in the CHANGELOG file in the GPlates source-code releases.
GPlates 1.4 compiles and runs on Windows 7/8/8.1, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.4 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2013-10-22: GPlates News Quarterly Updates
A newsletter regarding recent GPlates related research, information on tutorials, new GPlates compatible data and plate models, and other news from the research group is now available at GPlates News Quarterly Updates. This is the first in a series of quarterly newsletter updates so please subscribe at GPlates News Quarterly Updates to receive these regular updates.
2013-05-29: GPlates 1.3 released
What's new in version 1.3:-
- Integration of Orange and GPlates as a data mining toolkit suite.
- Includes Orange widgets to obtain pre-processed (co-registration) data from GPlates via network socket requests.
- New GPlates Rotation (GROT) file format:
- Extends PLATES4 rotation format to include a much richer set of metadata attributes.
- Please visit the GPlates Rotation (GROT) page for more details.
- Surface relief lighting:
- Visually transpose one raster onto another in the form of relief/height map shading.
- Volume visualisation of 3D scalar fields (early preview functionality):
- Developed in collaboration with Tobias Pfaffelmoser (Technical University Munich).
- For more details please see A Custom Implementation for Visualizing Sub-surface 3D Scalar Fields in GPlates
- To be officially released in GPlates 1.4.
- This release (1.3) contains preview functionality available to advanced users:
- Requires the "--enable-scalar-field-import" command-line switch to enable scalar field import.
- For example, "cd C:\Program Files (x86)\GPlates\GPlates 1.3.0" and "gplates-1.3.0.exe --enable-scalar-field-import".
- Enables menu item 'File -> Import -> Import 3D Scalar Field...'
- SVG export includes rasters, 3D scalar fields and filled polygons.
- Export arbitrary resolution rasters (eg, 3,000 x 3,000 pixels).
- Support for reading the OGRGMT file format ('.gmt').
- New finite rotation calculator utilities.
- New velocity imports/exports:
- Velocity domain generators for Terra and Lat/Lon meshes.
- Export velocities to Terra (text), CitcomS global and GMT formats.
- Calculate velocities in "Calculated Velocity Fields" layer:
- 'of domain points' - calculate velocities of reconstructed points.
- 'of surfaces' - calculate velocities of surfaces that intersect domain points.
- Enhanced velocity arrow display controls including screen space density and arrow scaling.
- New topological 'line' tool creates dynamic polylines.
- Canvas tools grouped into workflow tabs.
- Centralised GPlates Geological Information Model (GPGIM):
- GPGIM stored in a single XML file.
- All GPlates dialogs now conform to this central GPGIM.
- Features can now have either topological (dynamic) geometries or static geometries.
- Upgrades to Manage Feature Collections dialog including sort-by-filename and group selections.
- GPlates now contains a small assortment of commands (on the command-line):
- Commands are specified on the command-line and do not invoke the graphical interface of GPlates.
- Run GPlates with "--help" to list the commands and the options available to each command.
- However, in future, we will be recommending our GPlates Python programming interface (work in progress).
- Filled polygons in 2D map views.
- Improved filled polygon performance.
- Filled polygon opacity and intensity controls.
- Raster reconstruction now works with 'self-intersecting' polygons:
- Should mostly fix holes in reconstructed rasters due to missing polygons.
- 'age' colour palette button in raster layer (to use when loaded raster is an age grid).
...and many other changes that are listed in the CHANGELOG file in the GPlates source-code releases.
GPlates 1.3 compiles and runs on Windows 7/Vista/XP, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.3 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
Coming soon in GPlates...
Some of the new features coming soon to GPlates are:-
- Volume visualization of 3D scalar fields:
- Visualize scalar field as isosurfaces or 2D vertical cross-sections.
- Import scalar field from a sequence of 2D depth layers/rasters.
- Raster surface lighting:
- Visually transpose one raster onto another to combine details of two rasters.
- One raster generates colour and the other acts like a heightfield to generate lighting.
- And many other features including:
- New topological line tool to support construction of topological features using other topologies.
- Improved PLATES-based rotation file format providing richer metadata attributes.
- Export arbitrary (eg, 3,000 x 3,000 pixels) rasters to SVG and PNG/JPEG/etc.
- Export to a variety of velocity formats including Terra, CitcomS and GMT.
- Better integration of GPlates Geological Information Model (GPGIM) throughout GPlates.
Please see Conference publications for examples using GPlates volume visualization.
2012-10-24: GPlates wins NeCTAR/ANDS #nadojo competition.
Congratulations to GPlates team on winning this year's NeCTAR/ANDS #nadojo competition. The award-winning work demonstrated a new web-enabled GPlates prototype on the NECTAR/ANDS eResearch computing infrastructure, porting some of the powerful plate reconstruction capabilities to the web. The new GPlates competed with several other candidates from universities and research institutes in Australia, and winning on the basis of the novelty and future potential. A judge was quoted as saying: "...being able to look at tectonic plates and how they move over 140Ma years ago brought me back to that child-like awe of wonder and amazement, like the first time you look up at the stars and realise how many (light?) years away they are..." Well done GPlates team!
2012-01-30: GPlates 1.2 released
What's new in version 1.2:-
- New Small Circle tool:
- Create small circles directly on the globe or map using the mouse.
- Create small circles by specifying the centre and radii, and generating the centre from a stage pole if desired.
- Create small circle features which can be: exported to gpml, imported from gpml, and visualised as a layer.
- Query and edit small cirles through the Click Feature canvas tool.
- The Total Reconstruction Sequence dialog has been extended to allow:
- Creation, editing and deletion of Total Reconstuction Sequences (TRSs).
- Saving TRSs to existing rotation files, or to a new rotation file.
- Rasters can now be visualized in the map views:
- Supports all raster variations (reconstructed, time-dependent, age-grid and combinations of these).
- Raster opacity (and intensity) can be adjusted per layer to control semi-transparency.
- Python colouring (see user manual for details):
- Power users can create/register their own Python colouring scripts.
- Can use preliminary Python Application Programming Interface (API) to query feature properties.
- Option to dateline wrap Shapefiles when saving and exporting.
- New Log dialog displays low-level debug, warning and error messages.
- New Preferences dialog provides an interface to view and modify settings and parameters used in GPlates.
- Improved interactivity for very high resolution rasters (eg, approx. 1 minute resolution).
- New GPlates raster streaming tiled file format (files ending with ".gplates.cache").
- Clone Geometry tool can clone topological plate polygons.
- The Calculate Rotation Pole tool has its field automatically filled from an already-selected pmag VGP.
- Fixed slow saving to Shapefiles.
- Fixed rotation taking the longer path around a pole on rare occasions.
- Fixed holes appearing in large filled polygons.
- Fixed extremely long running time for Assign Plate ID assignment.
- Fixed exponential loading times when restoring many files during a session restore.
- ... Plus a number of other improvements and bug fixes.
GPlates 1.2 compiles and runs on Windows 7/Vista/XP, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.2 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2011-07-04: GPlates 1.1.1 released
Many bugs were fixed in version 1.1.1:-
- Added back missing age-grid smoothing of raster reconstruction.
- Fixed a number of issues with session save/restore of pre-1.1 sessions.
- Fixed a number of focused feature highlights issues including:
- Losing highlight when reconstruction time changes.
- Other geometries associated with focused feature not getting highlighted.
- Fixed a number of problems building/editing topologies:
- Topological sections not getting inserted.
- Incorrect auto-segment reversal.
- Inability to add same topological section more than once to topological boundary.
- Inability to add point geometries to boundary of topological network.
- Fixed a few update issues including:
- Globe not updating after changing the anchor Plate ID.
- Resolved topological boundaries not updated after editing a boundary feature's geometry.
- Filled polygons related fixes include:
- 'Fill polygons' option toggling wrong layer.
- Filled polygons rendered as square tiles for high zoom levels.
- Small improvement in rendering speed.
- A few export related issues including:
- Not exporting full motion path.
- Option to export resolved topologies to OGRGMT format removed (not supported).
- OGRGMT format now supports option to export to a single file.
- Resolved topologies not exporting when only "Export each Plate Polygon to a separate file" checkbox is ticked.
- Missing export of topological network boundaries.
- Inappropriate default directory for exported files.
- Exporting a single snapshot now does not modify current animation range.
- A couple of feature creation bugs fixed:
- Fixed incorrectly creating a conjugate isochron feature when creating a mid-ocean ridge feature is created.
- Fixed incorrectly adding a 'reconstruction' plate ID and conjugate plate ID to a new mid-ocean ridge feature.
GPlates 1.1.1 compiles and runs on Windows 7/Vista/XP, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.1.1 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2011-05-21: GPlates 1.1 released
What's new in version 1.1:-
- The Recent Session menu can now restore the layer connections you were using.
- Can display filled polygons for dynamic and static polygons (per-layer).
- Added new OGRGMT file format ('.gmt') compatible with OGR library and ogr2ogr tool.
- Improvements to topology build/edit tools including:
- Ability to add sections to interior and boundary of topological networks.
- Options to visualise triangulations associated with each network.
- Velocity layers now calculate velocities inside static polygons (in addition to topological plate polygons).
- Velocity layers can now calculate velocities at the vertices of polyline/polygon geometries.
- Can now load and display higher resolution rasters, including up to 0.3 minute resolution global rasters for the JPEG format.
- GPlates fitted with a novel cube 'loose' quad tree spatial partition, supporting region-of-interest queries, fast insertion of reconstructed geometries, hierarchical visibility culling.
- Improved layers user interface including:
- A button (in top-right of Layers dialog) to open the Colouring dialog.
- Layers grouped by layer type.
- A 'tick' icon for 'Reconstruction Tree' layers to toggle default layer.
- Can prevent the default 'Reconstruction Tree' layer from changing when opening a new rotation file.
- Improved file load/unload performance when many compute-heavy files already loaded - for example, dense velocity mesh cap files.
- Improved export dialog general user interface.
- New export options to control granularity of exports.
- New OGRGMT exports for reconstructed geometries, flowlines and motion paths.
- Export resolved topologies to Shapefile format.
- Improved rendering performance for flowlines.
- ... Plus a lot of other behind-the-scenes work to prepare for exciting future functionality.
GPlates 1.1 compiles and runs on Windows 7/Vista/XP, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.1 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2010-12-20: GPlates 1.0.0 released
What's new in version 1.0:-
- The ability to create and visualise flowlines and motion paths of points across plates.
- A new Small Circle tool, to help visualise stage rotations.
- When closing, GPlates will remember the files that you had loaded. The new Recent Session menu allows you to re-open files from a previous session.
- The viewport can now be annotated with text including the current reconstruction time.
- The background colour of the globe and graticule resolution can be configured.
- Layers can now be toggled on and off in the Layers dialog.
- The default Rotation layer can also be controlled directly from the Layers dialog.
- A preview of a new Total Reconstruction Sequences dialog to enable more powerful control over the rotations.
- ...as well as a host of other improvements throughout the application.
GPlates 1.0 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Download GPlates 1.0 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2010-08-31: GPlates 0.9.10 released
This release is a preview of raster reconstructions and layers. We have implemented raster reconstructions to take advantage of the majority of graphics systems so please let us know if you are having difficulty on your system.
If you want to reconstruct a raster, and try out the new layers system, the sample data in this release contains the following files to demonstrate this:
-
present-day plate polygons (in
SampleData/FeatureCollections/StaticPolygons/) -Global_Earthbyte_GPlates_PresentDay_PlatePolygons_20100826.gpml, -
a rotation file (in
SampleData/FeatureCollections/Rotations/) -Global_Earthbyte_GPlates_Rotation_20091015.rot, -
a global marine gravity raster (in
SampleData/Rasters/) -DNSC08GRA_6m.gpml, -
an ocean-floor age grid (in
SampleData/Rasters/) -agegrid_6m.gpml.
To reconstruct the above gravity raster load all the above files into GPlates using "Open Feature Collection" from the "File" menu. And then connect the present-day plate polygons to the "Polygon features" input channel of the gravity raster. The gravity raster should now reconstruct.
For a high-detail reconstruction you can also connect the age grid raster to the "Age grid feature" input channel of the gravity raster.
With the release of GPlates 0.9.10, we have prepared a video presentation introducing all the new features which are now available:-
- A completely new Raster Import workflow
- Cookie-cutting of rasters with polygons
- The new Layers dialog
- Age grid support
- NetCDF grid support
- Half-stage rotation reconstruction method
- Snap nearby vertices tool
GPlates 0.9.10 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Qt 4.4.0 (or above) and CMake 2.6 are required. Download GPlates 0.9.10 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2010-05-03: GPlates 0.9.9 released
Changes since 0.9.8:
-
New paleomagnetic functionality including the ability to:
- create a Virtual Geomeomagnetic Pole (VGP) feature,
- generate a total rotation pole adjustment between the VGP and the geographic pole,
- specify when Virtual Geomeomagnetic Pole features are displayed.
-
Colouring improvements including the ability to:
- preview the effects of each colouring option,
- load colour tables from GMT CPT files for user-defined colouring,
- change colouring globally or per feature collection.
- New tools to delete, split and clone features.
-
Support for "unsaved changes" to feature collections:
- highlight feature collections with unsaved changes in red,
- new icons in the GPlates main window to indicate unsaved changes and file loading errors,
- exiting GPlates brings up a dialog with options to save unsaved changes.
-
Export improvements:
- all exports (including time-sequence and single snapshot exports) have been unified into a single dialog,
- new export method: - export the globe view as a single image (or time-sequence of images),
- new export method: - export total rotation poles for each plate id relative to the anchor plate or relative to the next plate in the circuit,
- filenames of exports (notably time-sequence exports) can have parameters (such as reconstruction time) inserted in them.
- Generate CitcomS 3.1 meshes inside GPlates.
-
Cookie-cutting and plate id assignment has been extended:
- to regular static polygon features (in addition to topological closed plate boundary features),
- to assign time of appearance/disappearance (in addition to plate ids).
-
Topological closed plate boundary improvements including:
- automated reversal of topological line sections,
- support for feature ids in Shapefiles,
- more flexibility when adding topological line sections (such as adding same section multiple times to a boundary).
- Option to rotate daughter/children plates in the "Modify Reconstruction Pole" tool.
-
Other improvements including:
- conjugate plate id option in "Create Feature" dialog for the relevant features,
- read/write 4-digit plate ids from/to PLATES line format files,
- multipoint support in PLATES line format (eg, hotspots),
- root of time-dependent raster filenames can vary, for example, "imageA" and "imageB" in "imageA-0.jpg" and "imageB-1.jpg".
GPlates 0.9.9 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Qt 4.3.2 (or above) and CMake are required. Download GPlates 0.9.9 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2009-12-17: GPlates 0.9.8 released
Changes since 0.9.7.1:
- The new 0.9.8 release of GPlates can use a loaded topological plate polygon data set to "cookie-cut" a feature collection and assign Plate IDs to the data based on which plate polygon intersects them. This enables users to load data files that do not have Plate ID or reconstruction time information, and then manipulate that data with the loaded reconstruction model.
-
Support for virtual geomagnetic pole data is ongoing. As a special preview of GPlates paleo-mag functionality, GPlates is now able to import data from the IAGA Global Paleomagnetic Database created by Mike McElhinny and Jo Lock, later maintained by Sergei Pisarevsky. GPlates can then assign Plate IDs from a topological plate polygon data set and then display the reconstructed virtual geomagnetic pole locations on the globe. The database is available online here: http://www.ngu.no/geodynamics/gpmdb/In future releases, full editing capabilities and support for a wide range of data (such as the MagIC database) will be forthcoming.
- Small circle arcs can be rendered by GPlates to indicate the error bounds of virtual geomagnetic poles.
- Development on new colouring options has started. GPlates' default Plate ID colouring scheme has been tweaked, and a new colour by Plate ID region colouring scheme has been created.
- The Modify Reconstruction Pole tool can now constrain the latitude of the pole manipulation while interactively making adjustments.
- The topological capabilities of GPlates are undergoing constant improvement and expansion. As a consequence of these ongoing developments, GPlates now links with CGAL, the Computational Geometry Algorithms Library. This will enable many impressive extensions to the topology tools in the future.
GPlates 0.9.8 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Qt 4.3.2 (or above) and CMake are required. Download GPlates 0.9.8 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2009-11-10: GPlates 0.9.7.1 released
Changes since 0.9.5:
- GPlates can now utilise a full screen mode, which is available by pressing F11. This mode is ideal for presenting data and animations using GPlates. It makes the user interface more minimalistic, granting a greater amount of screen space to the main view. This is especially useful on low-resolution devices such as projectors.
- A new Measure Distance Tool has been implemented, allowing precise measurement of the distance between any two chosen points. It also interacts with the digitisation and feature-selecting tools, to enable easy inspection of the distances along polyline geometries and polyline segments.
- Exporting the Total Reconstruction Poles table to CSV can now be done with a choice of delimiters, and more closely adheres to the CSV specifications.
- The previous 0.9.6 release involved the integration of the plate polygon closure workflow into the main stable branch of GPlates. With 0.9.7.1, additional work has gone into improving the user experience and making the topology algorithms more intelligent, and enables the export of geometry sub-segments involved in topologies.
GPlates 0.9.7.1 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Qt 4.3.2 (or above) and CMake are required. Download GPlates 0.9.7.1 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2009-06-17: GPlates 0.9.5 released
The massive GPlates 0.9.5 release in fact consists of two simultaneous software releases:
- the “official” release of the GPlates “stable mainline” (like all previous 0.9.x releases), named GPlates 0.9.5
- the “testing” release of the widely-anticipated extension functionality for continuously-closing plates and lithosphere velocity fields which was developed primarily at CalTech, named GPlates 0.9.5 + platepolygon-testing.
The GPlates 0.9.5 release features the following changes since 0.9.4:
- GPlates can now export feature data in the Shapefile format. (This complements the existing ability to import Shapefiles into GPlates as feature data.)
- Additionally, GPlates can now export “reconstructed geometries” (feature geometries at a particular reconstruction time in the past) in both the Shapefile and GMT formats.
-
GPlates is now able to display the Earth in a variety of map
projections (in addition to the existing 3-D Orthographic Globe
projection):
- Rectangular
- Mercator
- Mollweide
- Robinson
-
The advanced functionality of the new Export Animation dialog
enables you to harness the power of the GPlates reconstruction engine to create
your own “data animations”, exporting a sequence
of frames from an animation and saving it to disk in a sequence of files.
Currently, the Export Animation dialog offers the following export functions:
- all reconstructed feature geometries (as GMT .xy files or Shapefiles)
- a 2-D vector graphics snapshot of the view (as SVG files)
- all velocity fields (as GPML files)
- The GPlates main window has enjoyed a minor re-design of its layout, to improve the locality of the controls: Now the reconstruction-time controls are together above the reconstruction view, and the view controls (zoom, choice of map projection, and camera and mouse positions) are together below the reconstruction view. This re-design allowed us to incorporate an integrated animation time-slider in with the time controls.
-
GPlates is now released as a MacOS X binary bundle in a
.dmgfile (in addition to the existing Windows binary installer and the Linux/UNIX and Windows source-code packages). To install GPlates on MacOS X, simply:- double-click on the
.dmgfile to open the disk image in Finder, - drag the GPlates binary into your Applications folder.
- double-click on the
- It's now even easier than before to manipulate geometries interactively. When you're deciding which vertex you want to move using the Move Vertex tool, each vertex will light up yellow when you pass the mouse pointer over it, and the coordinates of the vertex also light up yellow in the Task Panel. You can move vertices of existing feature geometries or vertices of partially-digitised geometries.
- You can now insert vertices into the middle of an existing feature geometry, or even extend the feature geometry at either end, using the new Insert Vertex tool. If the mouse pointer is over a line-section of the geometry, the line-section will light up, and you can click the mouse button once to insert a new vertex. If the mouse pointer is past either end of the geometry, you can click once to extend the geometry from that end.
- You can also delete a vertex from a geometry using the new Delete Vertex tool. The geometry which will be deleted will light up red, and the coordinates of the geometry will also light up red in the Task Panel.
- GPlates offers Better handling of multi-geometries (multiple-geometries per feature): both in the loading and saving of files; and in the feature focus and canvas tools in the user-interface.
- The official GPlates user-manual is now online!
The GPlates 0.9.5 + platepolygon-testing release builds upon the simultaneous GPlates 0.9.5 “stable” release, adding the following advanced extension functionality:
- continuously-closing plates, utilising the new topological geometry functionality for the construction of time-varying topological plate-boundary polygons
- the calculation of lithosphere velocity fields, utilising the calculation of plate-motion velocities at CitComS mesh-node locations
- velocity-field arrow decorations — which are zoom-dependent, so that both the size of the arrows and the visual density of the arrows (i.e., the number of arrows drawn on the visible area of the surface of the Earth) scale automatically with zoom
- the new Topology Sections table which displays, and enables tabular editing of, topologies
- automated generation and export of velocity fields as GML DataBlock instances
GPlates 0.9.5 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Qt 4.3.2 (or above) and CMake are required. Download GPlates 0.9.5 from the Download page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Download page.
2008-12-23: GPlates 0.9.4 released
Changes since 0.9.3:
- The transition to the CMake build system has been completed. This new build system replaces both the Autoconf/Automake/Libtool-based build system for Linux and the project files for the MS Visual Studio compilers, in addition to enabling compilation on MacOS X.
- GPlates now compiles and runs on the three main desktop operating systems: Windows, Linux and MacOS X.
- It is now possible to manipulate geometries interactively, dragging vertices using the new Move Vertex tool. This tool can be used on both existing feature geometries, as well as geometries which are in the process of being digitised. When the tool has been selected, the selected geometry will be drawn in grey, while its vertices will be highlighted and draggable.
- Previously, a raster image would always be shown by GPlates to cover the whole globe, from -180 to +180 degrees longitude and -90 to +90 latitude. It's now possible to specify a surface extent of any longitude and latitude range for the raster, enabling rasters of a smaller size to be correctly sized and positioned.
- The Manage Feature Collections dialog offers the ability to reload a file from disk with a single click, as well as the ability to enable or disable a feature collection without unloading or reloading the file.
- It is now possible to save feature collections in GMT format, with a choice of header formats: PLATES4 line header; GPGIM feature properties; or a mixture of the two. It's also possible to export a digitised geometry in GMT format (it was already possible to export a digitised geometry in PLATES4 line-format) during the digitisation process, without needing to create a whole new feature.
- Shapefile attributes may now be edited in the Feature Properties dialog in the same way as native GPGIM property-values.
- The Task Panel can now be resized in the main window, enabling text fields to be widened in order to display longer lines of text.
- All the attributes in a Shapefile may additionally be viewed in a more compact tabular (spreadsheet-like) format, with one attribute per column.
GPlates 0.9.4 compiles and runs on Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux and MacOS X. Qt 4.3 (or above) and CMake are required. Download GPlates 0.9.4 from the Downloads page.
GPlates-compatible data have been made available. For more information, see the Downloads page.
2008-10-20: GPlates 0.9.3.1 released
Changes since 0.9.2:
- It is now possible to digitise new feature geometries using the point, polyline and polygon digitisation tools. After a feature geometry has been digitised, an easy-to-use wizard is provided for the creation of a feature, enabling the user to specify the basic properties of the feature such as plate ID, time of existence and name, as well as the feature collection into which the new feature should be placed.
- The new Modify Reconstruction Pole tool enables the interactive modification of the Total Reconstruction Poles which define a reconstruction. The user may drag the geometries of a plate around the globe to modify the Total Reconstruction Pole which reconstructs that plate. When the user is happy with the new position of the plate, he or she may click the “Apply” button to cause a dialog box to appear which lists the calculated finite rotations for review; if the user then clicks the “OK” button, a new Total Reconstruction Pole will be inserted automatically into the loaded rotation file at the appropriate reconstruction time.
- When a feature geometry is focused or a new feature geometry is being digitised, the geometry will be highlighted in white. When a geometry is dragged around the globe, its position will be updated in real time in grey.
- The Task Panel is a new user interface element in the main window which provides status information about whichever feature-interaction tool is currently active. Depending upon which tool is active, this information consists of: a summary of the feature (when the Choose Feature tool is active); a listing of the coordinates which have been digitised so far (when one of the digitisation tools is active); or the adjustment by which the Total Reconstruction Pole has been modified (when the Modify Reconstruction Pole tool is active).
- It is now possible to choose between different feature-colouring schemes (by feature-type, by feature age or by a single user-specified colour), in addition to the existing colouring by plate ID.
- The long-awaited GPML reader is now operational! This reader is able to read all reconstructable feature-types and reconstruction feature-types (Total Reconstruction Poles and Absolute Reference Frames) defined in the GPGIM 1.6 specification. GPML, the GPlates Markup Language, is the GML-based “native” file format of GPlates.
- The XML-conformance of GPML input, output and in-memory storage has been improved, to ensure GPlates handles XML namespaces correctly.
- GPML may be compressed or uncompressed as it is being written to file or read from disk, using the freely-available free software program GZip. GZipped GPML files can be up to 30 times smaller than uncompressed files!
- It is now possible to encode a variety of Shapefile attribute-types, with arbitrary attribute-names, in GPML.
- The internal geometry types, reconstruction mechanism and display graphics have been overhauled to enable GPlates to handle and display polygons and multi-geometries, as well as store duplicate vertices in polylines and polygons.
- Geometric property-values may now be edited in the Feature Properties dialog in the same easy-to-use fashion as non-geometric property-values.
The GPlates 0.9.3.1 release is a minor bugfix to GPlates 0.9.3, to fix a bug in the mapping of Shapefile attributes which was noticed after GPlates 0.9.3 was uploaded, but before any release announcement had been made. There are no other changes from 0.9.3.
Download GPlates 0.9.3.1 from the Downloads page.
GPlates 0.9.3.1 compiles and runs on Linux, Windows XP and Windows Vista. (Support for MacOS X is currently in testing — contact us if you'd like to participate in the testing process!) Qt 4.3 or above is required.
A GPlates-compatible global coastline file and a rotation file may be downloaded from the EarthByte Project Resources page. For more information, see the Downloads page.
A GPlates-compatible sequence of time-dependent global raster images (JPEG images, generated from GMT grid files of dynamic topography created by Bernhard Steinberger at the Norwegian Geological Survey) may be downloaded from the Norwegian Geological Survey FTP site. For more information, see the Downloads page.
2008-05-23: GPlates 0.9.2 released
Changes since 0.9.1:
- In addition to reconstructable features with point- and polyline-geometries, GPlates 0.9.2 is able to display raster images on the globe. These images can represent any kind of imagery or gridded data which covers the whole globe (with the image spanning the longitude range of -180 degrees to +180 degrees, and the latitude range of -90 to +90). GPlates is able to read raster images in the widely-used JPEG image format; once a raster is loaded, it is displayed as an OpenGL texture, enabling GPlates to remain responsive when the globe is rotated or the zoom is changed. (Currently, raster images are not reconstructed by GPlates.)
- GPlates is able to display time-dependent global raster images. The user can instruct GPlates to load a sequence of JPEG image files contained in a folder (each image in the sequence corresponding to a particular instant in geological time) and GPlates will display the appropriate image on the globe for the current reconstruction time. As the user changes the reconstruction time, the raster image on the globe will update accordingly.
- The Query Feature Properties dialog has been extended to enable the editing of GPGIM feature properties in an easy-to-use fashion (using a variety of custom-designed user-interface widgets for the various property types). Thus, GPlates now makes the transition from pure visualisation to editing as well. In addition, the reconstructed geometries of a feature can be displayed in parallel with the present-day geometries that are stored in data files.
- Enhanced synchronisation between the user-interface elements which display the properties of GPGIM features means that when a property is changed, the program will react instantly to update the presentation of the feature — whether the changed property was a text field (which will be updated in the "Clicked" feature table), the time-period of existence of the feature (which may cause the feature to appear or disappear at the current reconstruction time) or the reconstruction plate ID (which may cause the feature to change colour and move to a different reconstructed position).
- The new Total Reconstruction Poles dialog provides a variety of informative representations of the total reconstruction poles (finite rotations) for the current reconstruction time: tables of the relative and equivalent finite rotations for each plate ID in the hierarchy; a tree-like representation of the hierarchy of relative rotations; and the circuit between any plate and the user-specified stationary plate. This dialog also enables the export of the tables of finite rotations in CSV (comma-separated value) format.
- The ability to map attributes in a Shapefile to GPlates Model properties on a per-Shapefile basis enables local Shapefile attribute-naming conventions to be integrated seamlessly into GPlates usage. The user-specified mappings will be saved to disk automatically, enabling GPlates to remember mappings between sessions. The attributes can be mapped to different properties at any time.
Download GPlates 0.9.2 from the Downloads page.
GPlates 0.9.2 compiles and runs on Linux and Windows XP. Qt 4.3 or above is required.
A GPlates-compatible global coastline file and a rotation file may be downloaded from the EarthByte Project Resources page. For more information, see the Downloads page.
A GPlates-compatible sequence of time-dependent global raster images (JPEG images, generated from GMT grid files of dynamic topography created by Bernhard Steinberger at the Norwegian Geological Survey) may be downloaded from the Norwegian Geological Survey FTP site. For more information, see the Downloads page.
An animated screenshot of the new time-dependent raster image functionality in action (using EarthByte data and Bernhard Steinberger's dynamic topography raster images) may be found on the Screenshots page.